In the fast-paced world of business, data is king – and sometimes, you need a touch of unpredictability to really make it shine. Random numbers in Excel aren't just for fun; they're critical tools for everything from sales simulations and A/B testing to anonymizing sensitive data, performing robust hypothesis testing, and creating sophisticated statistical models. Understanding how to harness this power can transform your data analysis and decision-making capabilities.
Excel, powered by the robust Mersenne Twister algorithm since version 2010, offers several powerful functions to bring randomness into your spreadsheets. Whether you're a seasoned Excel user or just starting, mastering these tools opens up a world of possibilities for realistic simulations, unbiased selections, and advanced data manipulation. Let's dive into how you can generate random numbers, explore their many applications, and even look at how AI is revolutionizing this fundamental task.
The Core Functions: Your Toolkit for Randomness
Excel provides a trio of functions, each designed for slightly different random generation needs. Knowing when and how to use each one is key to efficiency and accuracy. While incredibly useful, these functions are "volatile," meaning they recalculate every time your worksheet changes – a characteristic we’ll address later.
RAND(): Generating Random Decimals
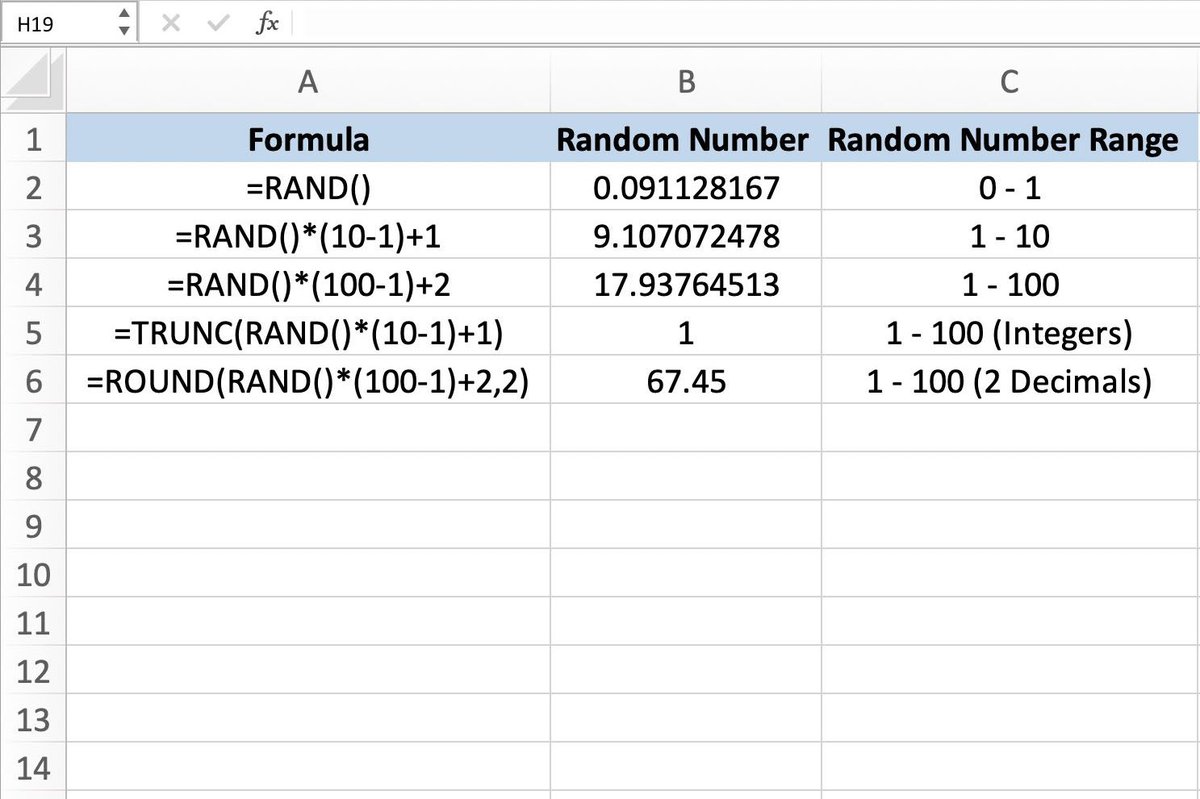
The RAND() function is your gateway to random numbers, producing a decimal value between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive). It's the most basic, yet incredibly versatile, of Excel's random number generators.
- Syntax:
=RAND() - How it Works: To get a random number within a specific range, you multiply
RAND()by the desired maximum value. For numbers between two values, sayaandb, the formula=RAND() * (b - a) + aoffers precise control. If you need integers, simply wrap these formulas within theINT()function. To grasp these fundamentals and more, explore our detailed guide on Basic Random Number Generation in Excel.
RANDBETWEEN(): Simplifying Integer Generation
When your needs call for whole numbers, RANDBETWEEN() streamlines the process beautifully. This function eliminates the need for nesting RAND() within INT(), making your formulas cleaner and more intuitive.
- Syntax:
=RANDBETWEEN(bottom, top) - Example:
=RANDBETWEEN(10, 20)instantly gives you a random integer between 10 and 20, inclusive. It's perfect for quickly populating data ranges with whole numbers, whether for testing or light simulations.
RANDARRAY(): Dynamic Arrays for Modern Excel
For users of Excel 365 and Excel 2021, RANDARRAY() is a game-changer. This dynamic array function lets you generate multiple random numbers simultaneously, specifying the number of rows and columns, the range, and whether the output should be whole numbers or decimals.
- Syntax:
=RANDARRAY([rows],[columns],[min],[max],[whole_number]) - This function can, for instance, create a 6x4 array of random integers between 10 and 20 with just one formula:
=RANDARRAY(6,4,10,20,TRUE). It's incredibly powerful for quickly setting up large datasets.
Beyond Basic Numbers: Advanced Randomization for Business Needs
Random numbers extend far beyond simple integers and decimals. They are crucial for solving specific business challenges, from unbiased selection to complex statistical modeling.
Generating Unique Random Numbers
Often, you don't just need random numbers; you need unique random numbers. Excel doesn't have a single direct function for this, but creative combinations get the job done. For example, in Excel 365/2021, you can combine UNIQUE() with RANDARRAY() (e.g., =UNIQUE(RANDARRAY(10,1,1,20,TRUE)) to get 10 distinct integers between 1 and 20). For more on unique numbers, specific distributions, and masking data for privacy, dive into Advanced Randomization Techniques and Functions.
Simulating Data with Specific Distributions
For statistical analysis and risk modeling, generating random numbers that conform to specific distributions (like normal distribution) is invaluable. You can combine RAND() with functions like NORM.INV() to achieve this. For instance, =NORM.INV(RAND(), 75, 10) can simulate scores with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 10. These capabilities are foundational for serious data work. Learn more about their applications in Simulations and Modeling with Random data in Excel.
Making Impartial Decisions and Selections
Need to randomly pick a winner, select a sample for a survey, or assign tasks fairly? Random number generation is your unbiased assistant. By combining RANDBETWEEN() with INDEX(), you can easily select a random item from any list. If you're looking to pick a random name from a list in cells A2:A10, a formula like =INDEX(A2:A10, RANDBETWEEN(1, ROWS(A2:A10))) does the trick. Discover more practical methods for this specific task in our guide on How to select random items.
Generating Random Dates, Times, and Text
Randomness isn't limited to numerical values. You might need to generate random dates for scheduling, random times for event simulations, or even random text strings for placeholder data. While the core random functions provide the numerical base, they can be cleverly combined with date, time, and text functions to create dynamic, non-numerical random data. To master these specific applications, explore our specialized article on how to Generate random dates, times, text.
Taming Volatility: Locking in Your Random Values
As mentioned, RAND(), RANDBETWEEN(), and RANDARRAY() are volatile. This means they recalculate every single time you make a change to your workbook. While useful for dynamic simulations, it can be frustrating when you need static values.
To "lock in" your random numbers:
- Select the cells containing your random number formulas.
- Copy the selection (
Ctrl + C). - Right-click on the same selected range and choose Paste Special > Values.
- Alternatively, for a single cell, you can select the cell, click inside the formula bar, and press
F9to replace the formula with its current value.
This simple step converts your dynamic formulas into static numbers, preserving them exactly as they were at the moment of copying.
The AI-Powered Way: Random Generation Without Formulas
Imagine generating complex random datasets without memorizing a single function or worrying about syntax errors. The rise of AI tools, such as Excelmatic, is transforming how we interact with spreadsheets, making advanced random number generation accessible to everyone.
Instead of wrestling with nested formulas, you can simply tell an AI agent what you need in plain language. For example, "Create a new column named 'Random IDs' and fill 100 rows with unique random integers between 10000 and 99999," or "Anonymize the 'Customer Account' column by replacing the first four digits with random numbers." The AI understands your intent, processes the request, and delivers the results directly into your spreadsheet.
This AI-driven approach eliminates the learning curve for formulas, reduces errors, and often produces static (non-volatile) results by default, saving you the extra step of locking in values. It empowers business professionals to focus more on analyzing their data and less on the technical implementation, unlocking faster insights and greater efficiency.
Looking Ahead
From foundational functions like RAND() to the dynamic capabilities of RANDARRAY(), Excel provides a powerful array of tools for random number generation. Whether you're conducting serious statistical analysis, running business simulations, or simply making an impartial decision, these features are indispensable. And with AI stepping into the arena, generating complex, random data is becoming simpler and more intuitive than ever before. Embrace these tools to bring new dimensions of realism and rigor to your data work.